Uncovering Evolutionary Mechanisms that Govern Meiosis

Meiosis is the process of cell division that creates sperm and eggs, which contain only half the genetic material of a regular cell. Understanding meiosis—how it’s regulated and how it differs across species—offers insight into evolution, development, and infertility.
Read about work from the Macfarlan Lab that improves understanding of meiosis.
Understanding the Synthesis of Collagen
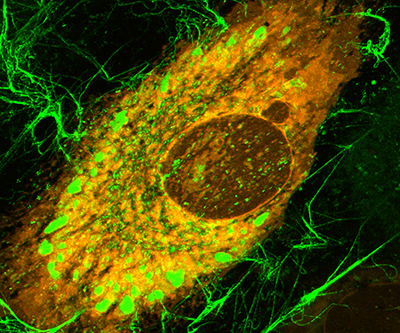
Collagen fibers provide the structural support for the body by forming the scaffolds of bones, skin, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and other tissues and organs. Collagen fiber synthesis is crucial for the health of normal tissues, and problems with it are linked to rare genetic diseases, as well as common disorders such as fibrosis and osteoporosis.
Read about work from the Leikin Lab that explains how cells produce and secrete collagen.
Finding New Treatments for Blood and Blood Pressure Disorders
Polycythemia and pulmonary hypertension are cardiovascular health conditions. Polycythemia occurs when the body makes too many red blood cells. Pulmonary hypertension occurs when blood vessels narrow and blood pressure increases within the arteries of the lung.
Read about work from the Rouault Lab on a new drug to treat polycythemia and pulmonary hypertension.
Understanding Molecular Switches that Control Cell Growth and Metabolism
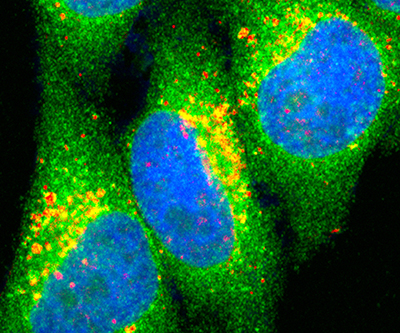
Cells use highly coordinated pathways to sense and adapt to their environment. For example, cells must change their metabolism when nutrients are not available. They switch from an active growth phase to a catabolic phase that breaks down existing sources of energy. A complex called TORC1 integrates various signals to control cell growth, proliferation, and cell death.
Read about work from the Lilly Lab on how TORC1 is regulated.
Decoding How Cells Migrate During Embryonic Development
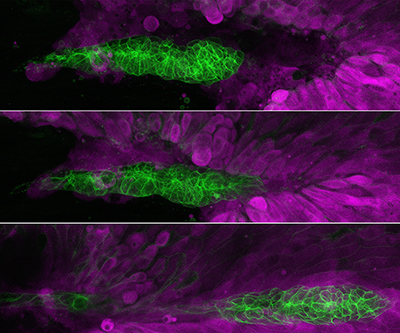
When an embryo develops, cell migration is a fundamental process that ensures the body forms properly. Problems with cell migration during these key stages of growth can lead to congenital anomalies and developmental disorders.
Understanding Factors that Protect the Brain During Stress

The brain, particularly the hippocampus, is sensitive to high levels of stress hormones called glucocorticoids that are released under stressful or traumatic circumstances.
Identifying New Targets for Male Contraceptives
Men have limited contraceptive options, namely condoms or sterilization. Researchers are studying new and better methods, including reversible drug therapies.
Read about work from the Dufau Lab on identifying new targets for non-hormonal male contraceptives.
Improving Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Assisted reproductive technology is used to help people conceive. It includes different types of fertility treatments and may use donor eggs, donor sperm, or previously frozen embryos.
Read about work from DIR researchers on improving assisted reproductive technologies.
Identifying Novel Cancer Treatments
Tumors rely on a cellular recycling system called autophagy to adapt and grow under low-nutrient conditions. Autophagy degrades existing cellular organelles and proteins to create sources of energy.
Read about work from the DePamphilis Lab on experimental cancer drugs that target autophagy.
Discovering Ways to Protect the Brain from Neurodegeneration
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by abnormal accumulation of a protein called alpha-synuclein (αSyn) in neurons.
Identifying Molecular Drivers of Leukemia
Leukemias are a type of cancer that occurs in blood cells, and they are the most common types of cancer in children. Some forms of leukemia can be very aggressive and hard to treat.
Back to Research Highlights from the Division of Intramural Research.
 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP