Attempting to Predict Shoulder Dystocia
Shoulder dystocia is a medical emergency that occurs when one or both of a baby’s shoulders get stuck during vaginal delivery. There is no clinically reliable method to predict the condition, which occurs in 0.2% to 3% of deliveries.
Understanding How School Food Availability Affects Students’ Eating Behaviors

Both the foods available at school and those available at food outlets in the surrounding neighborhood may impact an adolescent’s diet.
Identifying Placental-Related Genes that Regulate Birthweight
A fetus develops and grows in the womb for nearly 10 months, but the environment in which this occurs can set the stage for a person’s future health.
Read about work from the Epidemiology Branch on candidate genes that regulate birthweight.
Characterizing Dual-Function Small RNAs
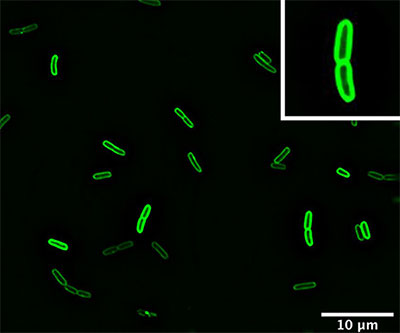
Small RNAs (sRNAs) help regulate gene expression—the degree to which genes are turned “on” or “off”—by interacting with messenger RNA. Some sRNAs encode a small protein in addition to this regulatory role.
Characterizing Immune Responses in Pregnancy
Infections during pregnancy can lead to poor health outcomes for the fetus and the pregnant woman. The bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a common cause of severe, life-threatening infections during pregnancy.
Identifying New Targets of Protein Synthesis Regulation
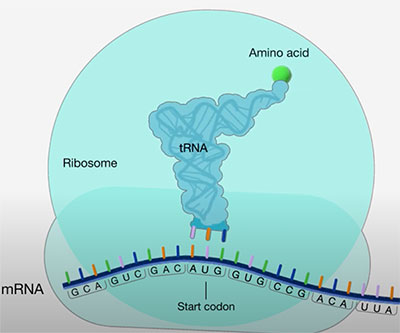
Translation—the reading of messenger RNA (mRNA) to make proteins—begins at an mRNA sequence called the start codon. Appropriate selection of the start codon by the cell’s translation machinery is crucial for proper protein synthesis.
Developing Novel Methods to Study Social Neuroscience
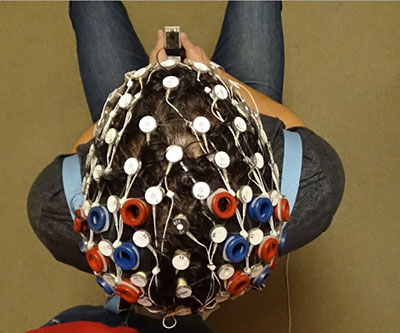
Researchers studying brain activity have a variety of tools to characterize neural activity, but there are limitations to each approach. Multimodal neuroimaging combines data collected from more than one technique, where one technique’s strength can help compensate for another’s weakness.
Delving into Risk Factors for Childhood Asthma and Allergy

The causes of childhood asthma and other allergic diseases are complex and not fully understood. Development of these conditions may be linked to early exposures, including the use of infertility treatments by the child’s parents.
Mapping the Role of RHOA in Vascular Development
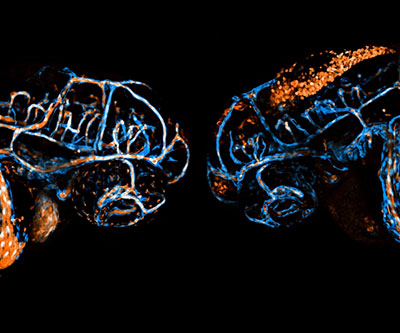
The protein RHOA is a master regulator of processes essential for development. However, its specific roles in vascular development—the formation of blood vessels—and the function of endothelial cells, which line blood vessels, are not clear.
Back to Research Highlights from the Division of Intramural Research: August 2022 Showcase.
 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP