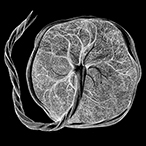
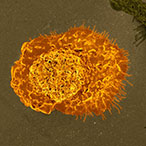
Science Update: Placental gene therapy corrects fetal growth complication in guinea pig model, according to NICHD-supported study
Researchers tested gene therapy in a guinea pig model of fetal growth restriction caused by placental insufficiency, which occurs when the placenta fails to provide enough oxygen and nutrients to the developing fetus. Currently, there is no treatment for this complication.
















 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP