Alcohol & Drug-Related Birth Defects Research at the NICHD
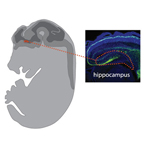
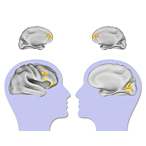
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), birth defects occur in one of every 33 babies and are the leading cause of infant death. These problems, present at birth, are caused by genetics, the environment, and other known and unknown causes. Environmental causes of birth defects include chemical and other exposures that occur during pregnancy, including exposure to alcohol and drugs.







 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP