Combining Therapeutic Strategies to Treat ALS
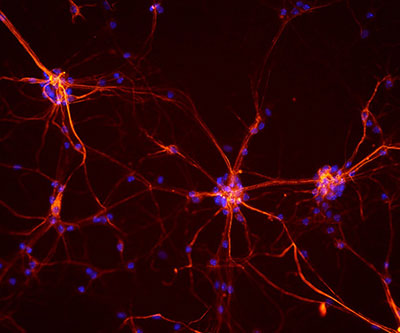
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease characterized by the gradual deterioration and death of motor neurons, the nerve cells responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movement. Currently, there are very few treatment options for ALS, and those that are available have limited efficacy.
Evaluating How Lipids Change During Early Pregnancy

Levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, and other blood lipids change during pregnancy and are critical for fetal development and a healthy pregnancy. Abnormal blood lipid levels are linked to adverse pregnancy outcomes and a higher risk for cardiovascular diseases in mother and child.
Evaluating the Safety of Anesthesia for Children with Rare Diseases
Analyzing biological samples from people with rare neurometabolic diseases helps scientists advance the understanding and treatment of these conditions. Collecting such samples may require research study participants to undergo sedation, but little is known about the effects of anesthesia on people with these diseases.
Understanding How Prefrontal Cortex Neuronal Activity is Coordinated
The prefrontal cortex is an important area of the brain that processes internal and external signals to produce goal-driven behaviors, including those affected by psychiatric and developmental disorders.
Advancing Understanding of a Key Protein for Nervous System Development
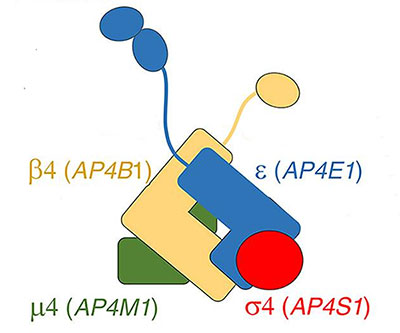
Mutations in the genes that provide instructions for the adaptor protein 4 (AP-4) complex cause a form of hereditary spastic paraplegia characterized by weakness and stiffness in the muscles of the lower and upper limbs, intellectual disability and seizures, and brain malformations.
Understanding the Role of “Jumping Genes” in Psychiatric Disorders
Transposable elements, sometimes called “jumping genes,” are DNA sequences that can move from one location to another. They’re estimated to make up nearly half of the human genome and are mostly inactive.
Improving Understanding of Legionella Infection
Legionella pneumophila causes Legionnaires’ disease, a serious form of pneumonia. Understanding how the bacterium multiplies within infected cells will aid development of treatment and prevention strategies for Legionnaires' disease and related illnesses.
Assessing Changes in Fibroids During Pregnancy
Uterine fibroids are the most common noncancerous tumors in women of reproductive age. Because fibroids are potentially linked to pregnancy complications, scientists are working to understand the changes that these benign tumors may undergo during pregnancy.
Identifying New Regulators of Bacterial Metabolism
Bacteria, including E. coli, have regulatory elements that boost survival when key nutrients like nitrogen are in short supply. Bacteria can alter their metabolic pathways to create new sources of nutrients or utilize different nutrients, creating contingencies against nutrient-poor environments.
Back to Research Highlights from the Division of Intramural Research: February 2023 Showcase.
 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP