Information Transfer by Voltage-Dependent Channels
Voltage-sensitive ion channels are crucially involved in information processing and transfer in humans and other multicellular organisms. Due to their small size and limited numbers, ion channels have to function in extremely noisy environment. This naturally creates the following question: Can ion channels and, generally, information transfer in the nervous system utilize ambient noise?
We answer this question by giving two positive examples wherein (i) noise is found to facilitate signal transduction by voltage-sensitive ion channels, thus demonstrating the phenomenon of the so called “stochastic resonance” in this system and (ii) random spike trains are used to create a hypothetical noise-based logic scheme for encoding and processing information by neuronal networks.
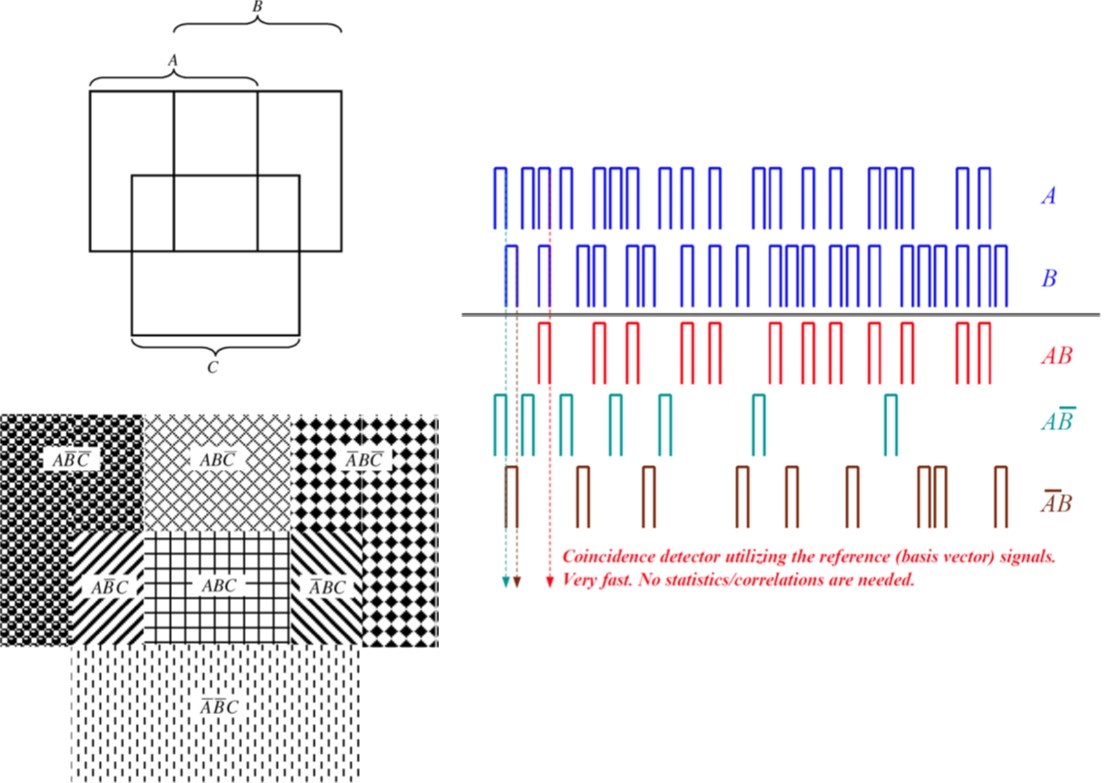
 Physics Letters A, 2009, 373:2338-2342, and L.B. Kish, C.G. Granqvist, T. Horvath, A. Klappenecker, H. Wen, S.M. Bezrukov. Bird’s eye view on noise-based logic. International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series, 2014, 33:1460363).
Physics Letters A, 2009, 373:2338-2342, and L.B. Kish, C.G. Granqvist, T. Horvath, A. Klappenecker, H. Wen, S.M. Bezrukov. Bird’s eye view on noise-based logic. International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series, 2014, 33:1460363).Publications:
L.B. Kish, C.G. Granqvist, S.M. Bezrukov, and T. Horvath. Brain: Biological noise-based logic. 
L.B. Kish, C.G. Granqvist, T. Horvath, A. Klappenecker, H. Wen, S.M. Bezrukov. Bird’s eye view on noise-based logic. International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series, 2014, 33:1460363.
L.B. Kish, S.P. Khatri, S.M. Bezrukov, F. Pepper, Z. Gingl, and T. Horvath. Noise-based deterministic logic and computing: A brief survey. 
S.M. Bezrukov and L.B. Kish. Deterministic multivalued logic scheme for information processing and routing in the brain. 
S.M. Bezrukov and L.B. Kish. How much power does neural signal propagation need? 
P.S. Ruszczynski, L.B. Kish, and S.M. Bezrukov. Noise-assisted traffic of spikes through neuronal junctions. Chaos, 2001, 11:581–586.
L.B. Kish and S.M. Bezrukov. Flows of cars and neural spikes enhanced by colored noise. 
S.M. Bezrukov. Stochastic resonance as an inherent property of rate-modulated random series of events. 
S.M. Bezrukov and I. Vodyanoy. Stochastic resonance in thermally activated reactions: Application to biological ion channels. Chaos, 1998, 8:557–566.
S.M. Bezrukov and I. Vodyanoy. Signal transduction across alamethicin ion channels in the presence of noise. Biophysical Journal, 1997, 73:2456–2464.
S.M. Bezrukov and I. Vodyanoy. Stochastic resonance at the single-cell level. Nature (London), 1997, 388:632–633.
S.M. Bezrukov and I. Vodyanoy. Stochastic resonance in non-dynamical systems without response thresholds. Nature (London), 1997, 385(6614):319–21.
S.M. Bezrukov and I. Vodyanoy. Noise-induced enhancement of signal transduction across voltage-dependent ion channels. Nature (London), 1995, 378(6555):362–364.
 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP